Monstera plants are renowned for their iconic fenestrated leaves, but their aerial roots are equally fascinating. This comprehensive guide explores the world of Monstera aerial roots, offering insights into their function, care, and even propagation.
Decoding Monstera Aerial Roots
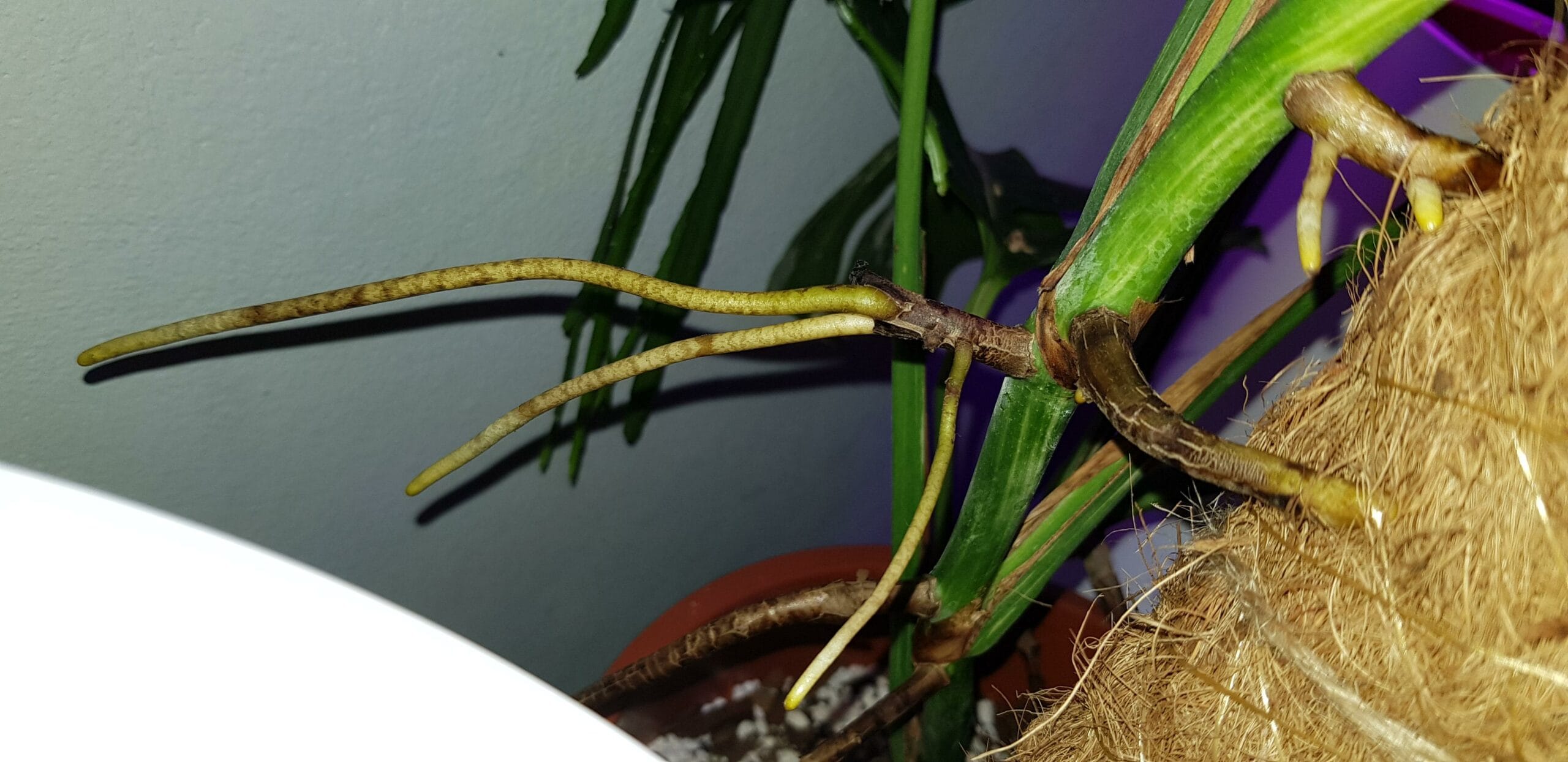
Monstera aerial roots are thick, rope-like extensions that emerge from the stem, trunk, or nodes. These roots, often appearing in clusters, are more than just aesthetic features; they play a vital role in the plant’s health and growth, especially in its natural habitat.
What are Monstera Aerial Roots?
In the wild, Monsteras use their aerial roots to climb trees, reaching for sunlight high in the canopy. These roots act like grappling hooks, anchoring the plant and allowing it to ascend. They also absorb moisture and nutrients from the humid air, supplementing the plant’s intake from the soil. While climbing is the primary function for a Monstera deliciosa (the most common variety), the moisture absorption capabilities of the aerial roots remain important, even in a home environment.
Managing Aerial Roots: A Multifaceted Approach
There are several ways to manage your Monstera’s aerial roots, each with its own advantages:
The Natural Look (Do Nothing): Leaving aerial roots untouched is perfectly acceptable. This is the easiest approach and allows the plant to express its natural growth habit.
Supporting Upward Growth (Provide Support): Providing a support structure, such as a moss pole, trellis, or sturdy stake, mimics the Monstera’s natural climbing behavior. Gently guide the aerial roots towards the support, and they will likely attach, leading to a more impressive, upright plant.
Boosting Stability and Moisture (Direct into Soil): Tucking longer aerial roots back into the pot’s soil can offer additional stability and access to moisture. This can be particularly helpful for larger, top-heavy Monsteras.
New Life from Cuttings (Water Propagation): Aerial roots on stem cuttings (with a node and at least one leaf) can aid in propagation. These roots help the cutting absorb water and establish itself more quickly, whether rooted in water or directly in soil. It’s crucial to remember that a lone aerial root in water will not grow a new plant; it needs the node and leaf for reproduction.
Taming the Wild (Pruning): Pruning overgrown or unruly aerial roots is perfectly safe. Use clean, sharp tools and cut close to the stem, taking care not to damage the main plant. While pruning might slightly reduce the plant’s stability, especially in taller specimens, providing a support structure can mitigate this.
Nurturing Your Monstera’s Well-being (with Aerial Roots)
Proper care is essential for a thriving Monstera:
- Watering: Consistent moisture (but not soggy soil) is key. This prevents the plant from over-relying on aerial roots for hydration.
- Humidity: Monsteras thrive in humid environments. Maintaining adequate humidity can actually reduce the number of aerial roots the plant produces. Misting or using a humidifier can be beneficial, especially in drier climates.
- Sunlight: Bright, indirect light is ideal. Too much direct sun can scorch leaves, while insufficient light can hinder growth.
- Health Checks: Regular monitoring of aerial roots is important. Look for signs of rot or disease, such as dark spots or mushy areas.
Repotting Your Monstera: A Root-Friendly Approach
Repotting a Monstera, especially one with prominent aerial roots, can seem daunting. However, with a little preparation and the right technique, it’s a manageable task.
Why Repot?
Repotting is crucial for a Monstera’s continued growth. When roots become pot-bound, they lack space to expand, hindering nutrient and water uptake. Repotting into a slightly larger container (1-2 inches wider) with fresh, well-draining soil provides the necessary room for root development and prevents growth stagnation.
Step-by-Step Repotting Guide
- Pot & Soil: Choose a pot with drainage holes and prepare a well-draining potting mix.
- Gentle Removal: Carefully remove the Monstera from its old pot, loosening the soil around the edges if necessary.
- Root Assessment: Examine the roots, gently loosening any circling or compacted roots.
- Placement: Position the Monstera in the new pot, ensuring the top of the root ball is level with the rim.
- Backfilling & Root Integration: Fill the remaining space with fresh potting mix, gently firming it. Carefully guide longer aerial roots into the soil, avoiding forceful bending or breaking. Shorter aerial roots can be left exposed or tucked around the base.
- Watering & Acclimation: Water thoroughly after repotting and place the plant in a location with bright, indirect light, avoiding direct sunlight for a few days.
Can I Cut Off Monstera Aerial Roots?
Yes, you can safely prune your Monstera’s aerial roots without harming it. While they contribute to the plant’s natural climbing ability and can absorb some moisture from the air, they are not essential for a potted Monstera’s survival. The plant gets most of its water and nutrients from the soil through its underground roots.
Why and How to Prune
Pruning aerial roots is primarily for aesthetic reasons, managing unruly growth, or preventing them from becoming a nuisance. Use clean, sharp pruning shears or a knife to cut the roots close to the stem, avoiding damage to the main plant.
Alternatives to Pruning
Instead of pruning, you can train aerial roots to grow onto a moss pole or other support, mimicking their natural climbing behavior. This creates a visually appealing display and encourages upward growth. You can also gently guide the roots back into the pot’s soil.
The Science of Aerial Roots: Ongoing Research
While much is known about aerial roots, research continues to explore their full potential and the nuances of their interaction with the environment. Some studies suggest that aerial roots may play a larger role in nutrient absorption than previously thought, and there is ongoing investigation into their potential interaction with microorganisms in the air. This highlights the complexity of plant biology and the potential for future discoveries.
Would you like to find out more about acceptance and commitment therapy hexaflex? Then click on the link provided to read more about it.
For more information about act hexaflex, you can go to the provided link and read more about it.
- Unlocking Francis Alexander Shields’ Finance Empire: A Comprehensive Biography - July 12, 2025
- Unveiling Francis Alexander Shields: A Business Legacy - July 12, 2025
- Francis Alexander Shields’ Business Career: A Comprehensive Overview - July 12, 2025













2 thoughts on “Monstera Aerial Roots: The Definitive Guide to Care, Propagation, and Troubleshooting”
Comments are closed.