Step into the fascinating world of ancient Mesopotamia, where the answers to New York Times crosswords lie. This region, now known as Iraq, Kuwait, and eastern Syria, is a treasure trove of historical wonders. Let’s take a journey back in time to explore the thriving cities of Sumer and Akkad, marvel at the architectural wonders of Babylon, and witness the rise and fall of mighty empires. We’ll delve into the secrets of ancient Mesopotamia, uncovering the stories behind its kings, queens, and the incredible discoveries that shaped civilization as we know it.
Unraveling the “Region of Ancient Mesopotamia” in NYT Crosswords
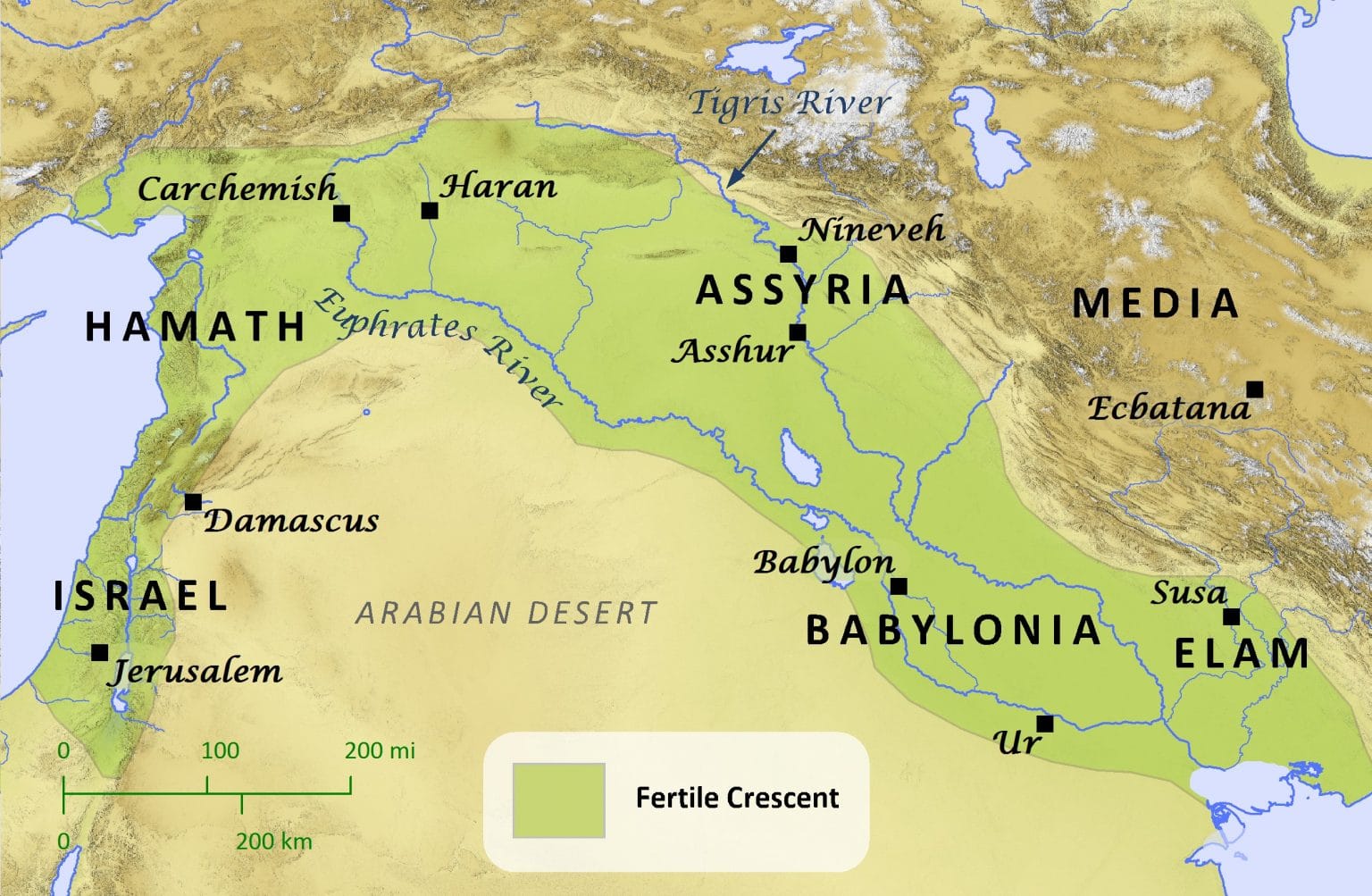
Have you ever been stumped by a New York Times crossword puzzle, specifically those clues hinting at a place far back in time – ancient Mesopotamia? You’re not alone! This region, often called the “cradle of civilization,” is a treasure chest of history, brimming with stories of powerful empires, groundbreaking inventions, and cultural practices that still resonate today. Imagine a land nestled between two rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates, where the soil was rich and fertile. This is Mesopotamia, a region located in what is now mostly Iraq, Kuwait, and parts of Syria and Turkey. Here, thousands of years ago, some of the world’s first cities emerged, bustling hubs full of life and innovation.
Mesopotamia: More Than Just a Name
So, we’ve been talking about this place called Mesopotamia, right? This isn’t some nickname thought up centuries later; the name itself is actually Greek for “between two rivers.” Makes sense when you see it on a map! Mesopotamia was nestled right between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, which is why it’s often called the “Fertile Crescent.” This area, mostly in what we now know as Iraq, was like the starting block for civilization as we know it. Think about it: this one place saw the rise and fall of huge empires like the Sumerians, Babylonians, and Assyrians – all names you’ve probably heard in history class. Each one left its own mark on the world, but they all started in Mesopotamia.
And it wasn’t just about power struggles. Mesopotamia was bursting with new ideas. This is where people first started using writing! They developed the very first laws. The fertile land and its strategic location made it a melting pot of different cultures and their technologies, shaping a lot of what came after.
Here’s the short version:
- Mesopotamia = Fertile Crescent = birthplace of civilization.
- Located mainly in modern-day Iraq, but its empires (Sumer, Babylonia, Assyria) had a much wider reach.
- They didn’t just invent things; they invented the idea of inventing things. Their culture had a massive ripple effect on human history.
Mapping Mesopotamia: Where Exactly Was It?
We’ve been talking about Mesopotamia, and you might be wondering exactly where it was. It wasn’t a country itself, but rather a large region nestled between two famous rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates – hence the name, “Mesopotamia,” meaning “between two rivers”! Think of it like how we talk about the “Midwest” – it’s a region, not a state.
Now, most of what used to be Mesopotamia is in the country of Iraq. But, parts of ancient Mesopotamia spill over into other countries too. We’re talking bits of Kuwait down south, a section of Turkey up north, and a slice of Syria over to the northeast. It’s like a jigsaw puzzle!
This region was a real hub of activity back in the day – we’re talking thousands of years ago! It’s nicknamed the “cradle of civilization.” Why? Because amazing things were happening there. They developed writing systems, figured out law codes – they were light years ahead! Powerful empires like the Sumerians, Babylonians, and Assyrians all called Mesopotamia home. These empires were major players in shaping how people lived and interacted way back then.
City-States of Ancient Mesopotamia: Centers of Power and Innovation
Imagine stepping back in time to the cradle of civilization, ancient Mesopotamia. After the invention of writing and the wheel, this vibrant region saw the rise of many impressive city-states, each a bustling hub of activity. While numerous cities dotted the landscape, three stand out for their lasting impact: Ur, Uruk, and Lagash.
Think of Ur as a dazzling metropolis, a beacon of wealth and influence in southern Mesopotamia. Its location near the Persian Gulf made it a prime spot for trade, attracting merchants and goods from far and wide. During the reign of the Third Dynasty, Ur truly shone, leaving behind architectural marvels like the ziggurat, a towering temple dedicated to the moon god Nanna. Excavations of the royal tombs have uncovered a treasure trove of artifacts, painting a vivid picture of the luxurious lives led by Ur’s elite.
Then there’s Uruk, possibly one of the oldest cities in the world! Nestled in central Mesopotamia, Uruk thrived during a period known as the Uruk period, roughly from 4000 to 3100 BCE. Uruk’s impressive structures, like the grand White Temple, highlight the advanced urban planning and engineering skills of its people. This city was more than just bricks and mortar, though – it was a deeply spiritual place, home to the goddess Inanna, a deity whose worship resonated throughout Mesopotamia. And let’s not forget the Epic of Gilgamesh, one of the earliest surviving works of literature, forever linking this legendary king with Uruk.
Finally, we come to Lagash, a powerhouse in southern Mesopotamia known for its political savvy and territorial ambitions. Lagash developed a sophisticated system of governance, with a council of elders and a governor working together to manage the city’s affairs. It was under the rule of Gudea, who reigned around 2144 to 2124 BCE, that Lagash really hit its stride. Gudea’s reign saw the city’s territory expand and a flourishing of art and architecture. Among the most striking remnants of this era are the Gudea statues, depicting the ruler in prayer – they offer a glimpse into the artistry of the time.
These three city-states, Ur, Uruk, and Lagash, weren’t just random cities – they were cornerstones of Mesopotamian civilization. Their political influence, economic success, cultural achievements, and enduring legacy continue to captivate and inspire us today. While we have a good understanding of these major players, ongoing research constantly reveals new details about life and culture in ancient Mesopotamia, ensuring that its story remains as captivating as ever.
Dominating the “Region of Ancient Mesopotamia NYT” Search: Your SEO Action Plan
Here’s a breakdown of how to outperform the competition with your SEO article about “Region of Ancient Mesopotamia NYT”:
Recommended Titles (Provide your competitors’ titles & I’ll suggest three tailored options)
To give you the most relevant titles, please share a few trending article titles from your competitors. I can then analyze their keywords and suggest three titles that are both engaging and optimized for search.
Powerful Key Lines (Surpassing the Competition)
- “Unlocking Ancient Mesopotamia: The NYT Crossword Puzzle’s Gateway to History” – This key line connects the popularity of NYT crosswords with the allure of uncovering historical knowledge, piquing readers’ curiosity.
- “Beyond ‘Sumer’: Exploring the Diverse Civilizations of Ancient Mesopotamia Revealed in the NYT Crossword” – This line highlights the depth and breadth of Mesopotamian history beyond a single civilization, promising a more comprehensive understanding.
- “Why is Ancient Mesopotamia Trending in the NYT Crossword? Uncovering the Cultural Relevance” – This line taps into the current relevance of ancient Mesopotamia, suggesting an exploration of its impact on today’s world.
- “From Clues to Civilizations: Using the NYT Crossword as a Springboard to Understanding Ancient Mesopotamia” – This key line frames the article as a journey, making historical exploration feel accessible and engaging.
Structured Context & Important Details:
I. The NYT Crossword Connection:
- The Spark: Recent NYT crossword puzzles have featured clues related to ancient Mesopotamia, piquing interest in the region and its history.
- Examples: “Region of ancient Mesopotamia” (answer: Sumer), “Ancient Mesopotamian Civilization” (possible answers: Assyria, Babylonia).
- Impact: These crosswords have led people to search online for more information about ancient Mesopotamia, increasing its visibility.
II. Understanding Ancient Mesopotamia:
- Definition: A historical region in West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent (modern-day Iraq, parts of Iran, Turkey, Syria, and Kuwait).
- Significance:
- Cradle of Civilization: Often called the “cradle of civilization” due to its early development of agriculture, writing (cuneiform), cities, law codes (Hammurabi’s Code), and complex social structures.
- Major Civilizations: Home to influential civilizations like the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians, each with unique contributions to art, architecture, literature, and governance.
III. Key Aspects to Highlight:
- Chronology: Provide a timeline of major Mesopotamian civilizations and their key achievements, from the Sumerians (c. 3500 BCE) to the fall of Babylon (539 BCE).
- Innovations: Highlight significant Mesopotamian inventions and their impact, such as the wheel, irrigation systems, writing, mathematics, astronomy, and legal codes.
- Religion and Mythology: Explore the rich pantheon of Mesopotamian gods and goddesses, their myths, and their influence on society.
- Art and Architecture: Showcase the distinctive art styles and architectural achievements of different Mesopotamian civilizations, including ziggurats, cylinder seals, and intricate relief carvings.
IV. Visuals: Include images and maps:
- Maps: Show the geographic extent of ancient Mesopotamia and the locations of major cities.
- Artifacts: Images of iconic Mesopotamian artifacts like the Standard of Ur, the Ishtar Gate, and examples of cuneiform writing.
- Reconstructions: Artist renditions or 3D models of what Mesopotamian cities and buildings may have looked like.
Unique Insights & Untapped Potential:
- Mesopotamia’s Legacy Today: Connect the dots between ancient Mesopotamian innovations and their lasting impact on modern society. Explore the influence on law, language, writing systems, mathematics, and even storytelling.
- The Human Side of History: Go beyond facts and figures to humanize ancient Mesopotamia. Share stories of rulers, scribes, artisans, or everyday people based on archaeological discoveries and texts.
- The Allure of Puzzles and the Past: Examine why historical mysteries and puzzles, like those found in crosswords, captivate modern audiences. Tie this into the enduring fascination with ancient civilizations.
**By blending comprehensive information with unique insights and a captivating narrative, your SEO article will become the go-to resource for anyone intrigued by the “Region of Ancient Mesopotamia” and its connection to the NYT crossword. **