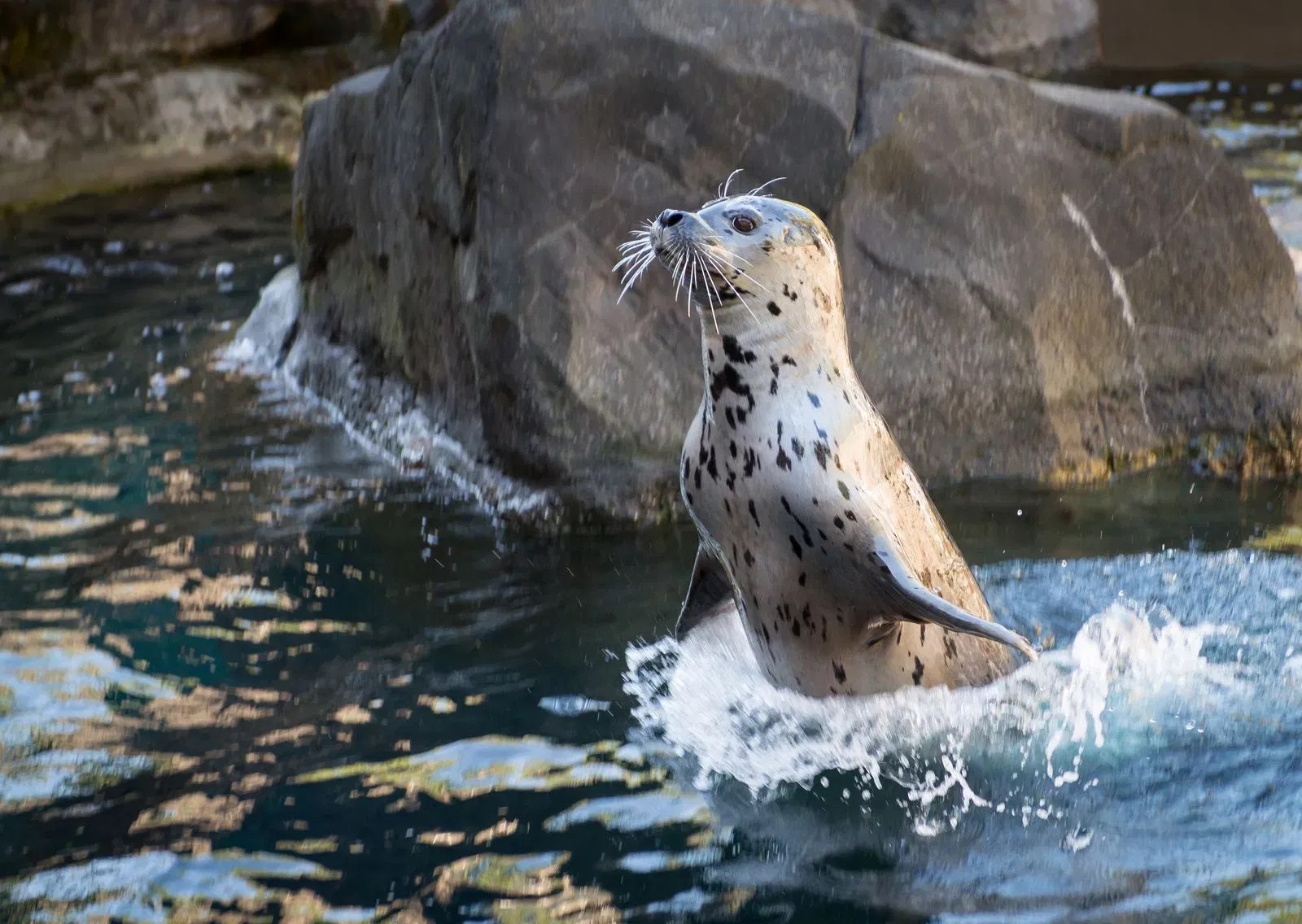
Ever watched a harbor seal gracefully disappear beneath the waves and wondered just how long they can stay submerged? These amazing creatures are natural-born divers, built to withstand the challenges of life underwater. But just how long can they hold their breath for, and what physiological marvels make this possible? Let’s dive deep into the secrets of harbor seals and their incredible breath-holding abilities.
How Long Can Harbor Seals Hold Their Breath?
Harbor seals, particularly the adults, are remarkable divers capable of holding their breath for an average of 30 minutes. This impressive feat far surpasses the average human’s breath-holding capacity of a minute or two. However, younger seals, like pups, are still honing their skills and can only manage a few minutes underwater.
The champion breath-holders of the seal world are the elephant seals, capable of remaining submerged for a staggering two hours! Their massive size allows for greater oxygen storage, contributing to their extended dives.
The Science Behind Harbor Seal Breath-Holding – Physiological Adaptations and Diving Depths
The secret to harbor seals’ impressive breath-holding skills lies in their remarkable physiological adaptations, honed by millions of years of evolution:
- Bradycardia (Slowed Heart Rate): When harbor seals dive, their heart rate plummets to a mere 4 to 6 beats per minute, drastically slowing their metabolism and conserving precious oxygen. This “diving reflex” ensures that oxygen is prioritized for essential organs.
- Optimized Respiratory Cycle: Harbor seals have a unique respiratory cycle that maximizes oxygen intake while minimizing wasted effort. They take a few quick breaths before diving, maximizing oxygen intake, and then enter apnea (breath-holding mode).
- Oxygen Storage in Muscles: Seals have a high concentration of myoglobin, a protein in their muscles that stores oxygen. This acts like an internal scuba tank, providing an extra oxygen reserve during dives.
- Reduced Blood Flow: While diving, harbor seals redirect blood flow away from non-essential organs, prioritizing the brain, heart, and muscles. This selective circulation ensures that the most critical functions remain oxygenated.
These adaptations, coupled with their streamlined bodies and powerful flippers, make harbor seals incredibly efficient underwater hunters and divers.
Factors Influencing Breath-Holding in Harbor Seals
Several factors beyond physiological adaptations can impact a harbor seal’s breath-holding duration:
Size
Larger seals, with their greater lung capacity and body mass, can store more oxygen, allowing for longer dives. This is why elephant seals, the largest of the seal family, can hold their breath for hours. Conversely, younger seals, still growing and developing their diving skills, have shorter dive times.
Water Temperature
Believe it or not, colder water temperatures actually benefit a seal’s breath-holding abilities. Cold water lowers a seal’s metabolism, reducing their oxygen demand and extending their dive time.
Behavior
Harbor seals are strategic divers. They’re not out for leisurely swims; each dive has a purpose, whether hunting for food or seeking shelter. This focused approach minimizes wasted energy and oxygen, contributing to longer dives.
Seals also know the importance of rest and recovery. When not diving, you’ll often find them hauled out on land or floating at the surface, catching their breath and recharging for their next underwater adventure.
Additional Factors and Interesting Facts
Here are some additional insights into the fascinating world of harbor seals and their breath-holding abilities:
- Hemoglobin: Harbor seals have a high concentration of hemoglobin in their blood, further increasing their oxygen-carrying capacity.
- Anaerobic Metabolism: In critical situations, seals can switch to anaerobic metabolism, producing energy without oxygen, though this is a short-term solution.
- Diving Depths: While harbor seals typically dive to depths of a few hundred feet, elephant seals can plunge to depths exceeding 1,500 feet!
The remarkable adaptations of harbor seals showcase the wonders of evolution, allowing these creatures to thrive in the challenging underwater world. If you’re eager to learn more about these fascinating creatures, dive into these articles: 10 interesting facts about seals and how seals communicate.
- Georgia Platform: A Southern Strategy, 1850s - March 31, 2025
- How many weeks is 40 days: Quick Conversion Guide for Accurate Results - March 31, 2025
- How many feet is 300 meters? 984 Feet: Understand Length Conversions Easily - March 31, 2025