Get ready for an exciting adventure as we dive into the fascinating world of igneous rocks, formed from the fiery depths of our planet. From towering mountains to mysterious ocean depths, igneous rocks have a wild story to tell. Let’s uncover their secrets, explore their incredible features, and discover how these rocks have shaped our world in amazing ways. Welcome to the captivating journey into the realm of igneous rocks!
Igneous Rocks Fun Facts
Ready to have your mind blown by igneous rocks? These aren’t just any old rocks; they’re like time capsules from deep inside the Earth, full of crazy stories and cool secrets. Let’s dive in and uncover some igneous rocks fun facts that will leave you feeling like a rockstar geologist!
From Volcanoes to Your Kitchen Countertop: Igneous Rocks are Everywhere!
Igneous rocks are like the chameleons of the geology world. You’ve got everything from the familiar granite of your kitchen countertop to the mysterious obsidian used by ancient cultures. Each type of igneous rock has its own unique origin story, shaped by the intense heat and pressure found deep within the Earth or during fiery volcanic eruptions.
Born of Fire: The Making of Igneous Rocks
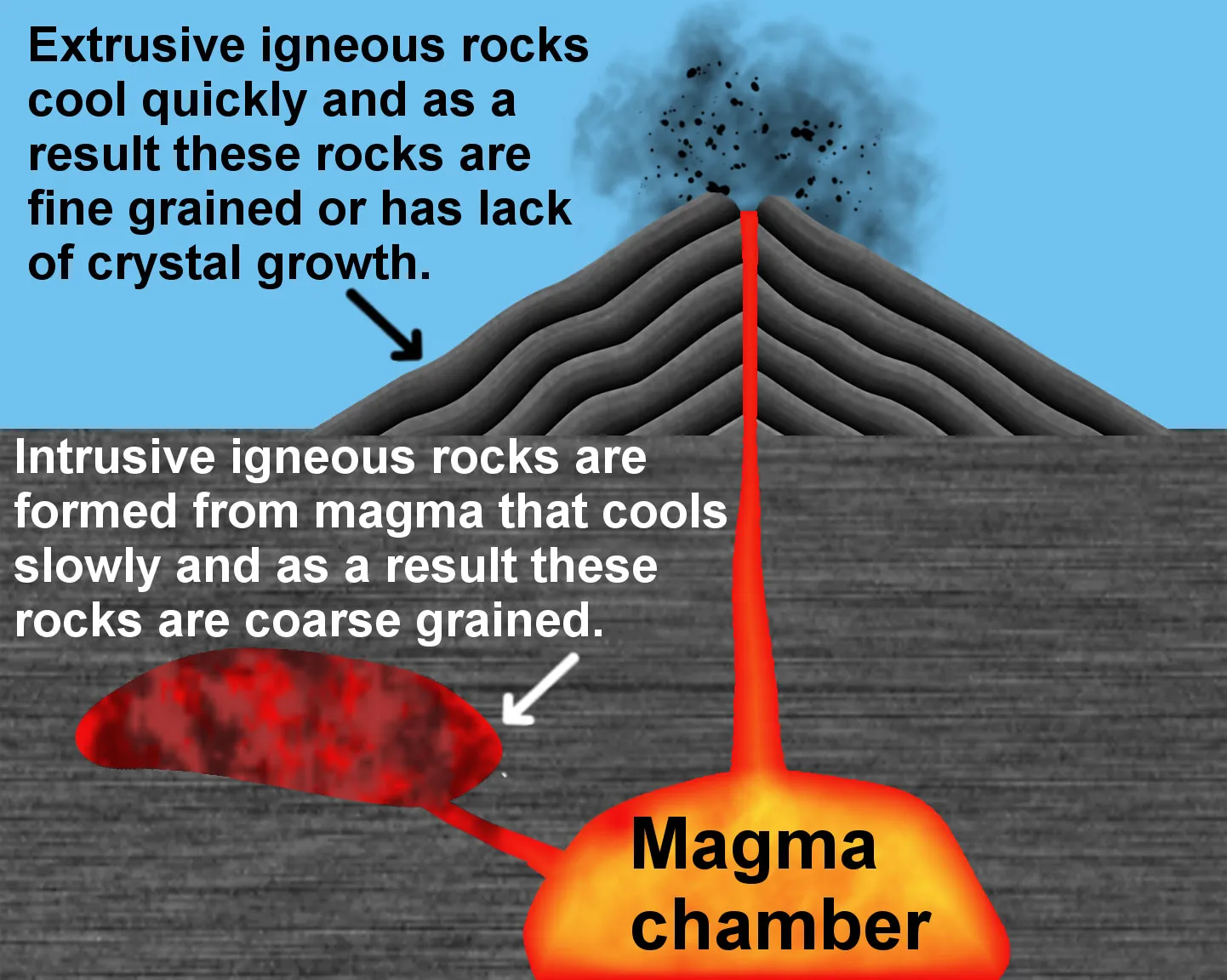
Imagine a bubbling cauldron of molten rock, known as magma, deep underground. That’s where igneous rocks get their start. Sometimes, this magma bursts onto the Earth’s surface as lava, creating amazing volcanic landscapes. But sometimes, it cools down slowly beneath the surface, forming intrusive igneous rocks with beautiful, large crystals.
A Rainbow of Minerals: What Makes Igneous Rocks So Unique?
Igneous rocks are like natural works of art, made up of a dazzling array of minerals. These minerals give each rock its own personality, influencing its color, texture, and even whether it sparkles! For example, granite often has shiny quartz crystals, while pumice, the rock that floats, is full of air bubbles.
Whispers from the Past: Igneous Rocks Tell Earth’s Story
Here’s a cool thought: igneous rocks are like ancient storytellers. They’ve witnessed incredible events over millions of years, from the formation of mountains to the movement of continents! By studying these rocks, scientists can piece together the history of our planet, like solving a giant jigsaw puzzle.
Get Ready to Be Amazed: Igneous Rock Fun Facts You Won’t Believe!
- Granite: The Kitchen Superstar – Ever wondered why granite countertops are so popular? This tough igneous rock is super durable and can handle almost anything you throw at it (well, maybe not literally throw things at it…).
- Obsidian: The Original Black Mirror – This dark, glassy rock was like a high-tech gadget for ancient civilizations. They used it to make sharp tools and even mirrors!
- Pumice: The Rock That Floats – You read that right, this rock can float! That’s because pumice is filled with air bubbles, making it super lightweight and perfect for exfoliating scrubs.
- Scoria: The Volcanic Snowflake – This rough and rugged volcanic rock looks like a snowflake frozen in time, with its jagged edges and bubbly texture. Talk about a cool souvenir from a volcanic eruption!
- Basalt: The Foundation of the Ocean – If you could take a walk on the ocean floor (wouldn’t that be amazing?), you’d mostly be walking on basalt. This dark igneous rock forms the foundation of the Earth’s oceanic crust.
The World of Igneous Rocks: A Neverending Adventure
Exploring the world of igneous rocks is like going on a treasure hunt through time. These rocks are full of surprises, from their fiery origins to their mind-blowing properties. So next time you see a rock, take a closer look – you never know what secrets it might hold!
Did you know that the most common extrusive igneous rock on Earth is basalt? It’s true! And that’s just one of the fascinating facts about igneous rocks that you can learn by clicking on the link.
What Is The Most Common Igneous Rock? The Surprising Truth About Earth’s Crust.
You might think, with all the diverse landscapes and rock formations on Earth, the most common igneous rock would be something exotic and rare. It’s actually quite the opposite! The champion is none other than granite, a rock we often see in everyday life. Remember those beautiful countertops in your kitchen or the impressive columns holding up historical buildings? Yup, that’s granite, a testament to its strength and durability.
Granite’s abundance isn’t just a coincidence. It hints at the powerful geological forces that have shaped our planet over millions of years. Imagine molten rock, known as magma, slowly cooling and hardening deep within the Earth’s crust. This process, happening over vast stretches of time, is how granite is born. So, next time you encounter this common yet remarkable rock, take a moment to appreciate the incredible journey it took from the fiery heart of our planet to the palm of your hand.
Can You Name 10 Types of Igneous Rocks? An Explosive Journey Through Earth’s Fiery Past
Key Takeaways:
- Igneous rocks result from the solidification of molten rock material referred to as magma.
- These rocks are categorized into two primary types: intrusive, formed below Earth’s surface, and extrusive, formed upon it.
- Their composition varies greatly, giving rise to a wide range of colors and textures.
- Granite, an intrusive rock, is widely used in construction due to its exceptional durability.
- Obsidian, an extrusive rock, has captivated ancient cultures who utilized it for crafting tools and mirrors.
- Pumice, another extrusive rock, is highly sought after for exfoliation purposes.
The Fiery Birth of Igneous Rocks
Imagine a fiery cauldron deep within the Earth, where molten rock churns and bubbles. That’s where igneous rocks get their start! This molten material, called magma, slowly cools and hardens. Sometimes it cools down deep underground, creating intrusive rocks like granite, which have big, sparkly crystals because they had plenty of time to form. Other times, the magma explodes onto the surface as lava, cooling quickly and forming extrusive rocks like basalt, which has a much smoother, finer texture.
Unveiling the Diversity of Igneous Rocks
The world of igneous rocks is incredibly diverse, with over 700 different types! Think of it like a giant rock collection, each with its own unique story to tell. Some, like granite, are tough and long-lasting, perfect for building things. Others, like obsidian, are glassy and sharp, used by ancient people for tools and even mirrors. And then there’s pumice, so light and porous because of all the air bubbles trapped inside, it actually floats!
Igneous Rocks: The Earth’s Building Blocks
Igneous rocks aren’t just pretty to look at—they’re the backbone of our planet! They make up a huge chunk of the Earth’s crust, forming the very foundation of our continents and ocean floors. By studying these fascinating rocks, geologists can piece together the Earth’s incredible history, like a puzzle stretching back billions of years.
Ready to Test Your Knowledge? Here are 10 Types of Igneous Rocks:
| Rock Type | Intrusive/Extrusive | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Granite | Intrusive | Coarse-grained, often light-colored, very hard |
| Basalt | Extrusive | Fine-grained, dark-colored, makes up much of the ocean floor |
| Rhyolite | Extrusive | Fine-grained equivalent of granite, often light-colored |
| Gabbro | Intrusive | Coarse-grained, dark-colored, similar to basalt |
| Andesite | Extrusive | Intermediate between basalt and rhyolite |
| Diorite | Intrusive | Intermediate between gabbro and granite |
| Peridotite | Intrusive | Dense, dark-colored, rich in iron and magnesium |
| Obsidian | Extrusive | Glassy, black or dark-colored, forms from rapid cooling |
| Pumice | Extrusive | Light, porous, often floats, used for exfoliation |
| Scoria | Extrusive | Dark-colored, porous, similar to pumice but heavier |
Volcanic vs. Plutonic: What’s The Difference? Uncovering The Secrets Hidden Beneath Our Feet
Volcanic and plutonic rocks are like siblings with the same DNA but totally different personalities. They both come from magma, that fiery soup brewing deep inside the Earth. But it’s their journey to the surface that sets them apart.
Think of volcanic rocks as the impatient ones. They’re formed when magma bursts onto the surface, usually in a dramatic volcanic eruption. This rapid cooling process doesn’t give the minerals much time to organize themselves, resulting in rocks with tiny crystals, sometimes even invisible to the naked eye. They’re like the “fast food” of the rock world.
Plutonic rocks, on the other hand, are the chilled-out siblings. They form when magma slowly cools and solidifies deep underground. This leisurely pace allows the minerals ample time to grow into large, well-defined crystals. They’re like the “slow-cooked meal” of the rock world, full of rich textures and flavors.
Here’s a handy table summarizing the key differences:
| Feature | Volcanic Rocks | Plutonic Rocks |
|---|---|---|
| Formation | Surface eruption | Underground cooling |
| Cooling Rate | Fast | Slow |
| Crystal Size | Small or microscopic | Large and visible |
So, next time you hold a rock, take a closer look. You might be holding a piece of Earth’s fiery past!
FAQ
Q1: What are some cool facts about igneous rocks?
A1: Igneous rocks hold a treasure trove of fascinating facts. They are forged from the molten heart of the Earth, presenting a captivating glimpse into our planet’s history. Some intriguing tidbits include their extreme temperatures of formation, ranging from a sizzling 700 to a mind-boggling 1,200 degrees Celsius. Additionally, they showcase a mesmerizing diversity of textures, from glassy obsidian to coarse-grained granite.
Q2: How do igneous rocks differ from other rock types?
A2: Igneous rocks stand out from their geological counterparts due to their unique birth story. Unlike sedimentary rocks, which form from the accumulation and cementation of sediments, or metamorphic rocks, which undergo transformation under intense heat and pressure, igneous rocks solidify directly from molten rock material. This fiery origin bestows upon them a distinct crystalline structure and captivating mineral compositions.
Q3: What are the different types of igneous rocks?
A3: The igneous realm is a tapestry of diversity, boasting a wide range of rock types. Two main categories emerge: intrusive and extrusive. Intrusive igneous rocks, nurtured within the Earth’s crust, cool slowly, allowing the formation of large, visible crystals. Extrusive igneous rocks, on the other hand, erupt onto the surface, cooling rapidly and resulting in fine-grained textures. From the stately granite to the volcanic basalt, each igneous rock bears a tale of its fiery origins.
Q4: Where can igneous rocks be found?
A4: Igneous rocks are not shy about making their presence known. They adorn the landscapes of all continents, from towering mountain peaks to the depths of the ocean floor. Their versatility extends to diverse geological settings, including volcanic terrains, mountain ranges, and even the foundations of continents. Additionally, these rocks play a crucial role in the formation of valuable mineral deposits, making them a treasure trove for geologists and miners alike.
Q5: What are some of the practical uses of igneous rocks?
A5: Igneous rocks are not just fascinating geological wonders; they also serve a multitude of practical purposes. Their inherent strength and durability have made them a cornerstone of construction materials, from ancient temples to modern skyscrapers. Basalt, a dark and fine-grained igneous rock, forms the foundation of many roads, providing a sturdy base for transportation. Granite, with its captivating crystalline structure, adorns countertops, monuments, and even sculptures, adding a touch of geological elegance to our surroundings.
- Unlocking 2-Letter Words with U: The Definitive Guide - April 4, 2025
- Unlock Words with the Letters THREE: Top Unscramble Tools 2025 - April 4, 2025
- Master Scrabble: X & Z Words for High Scores - April 4, 2025