Unraveling the Enigma of Post-Soviet Russia: Navigating the complexities of Russia’s transformation in the aftermath of the Soviet Union’s collapse.
Key Takeaways:
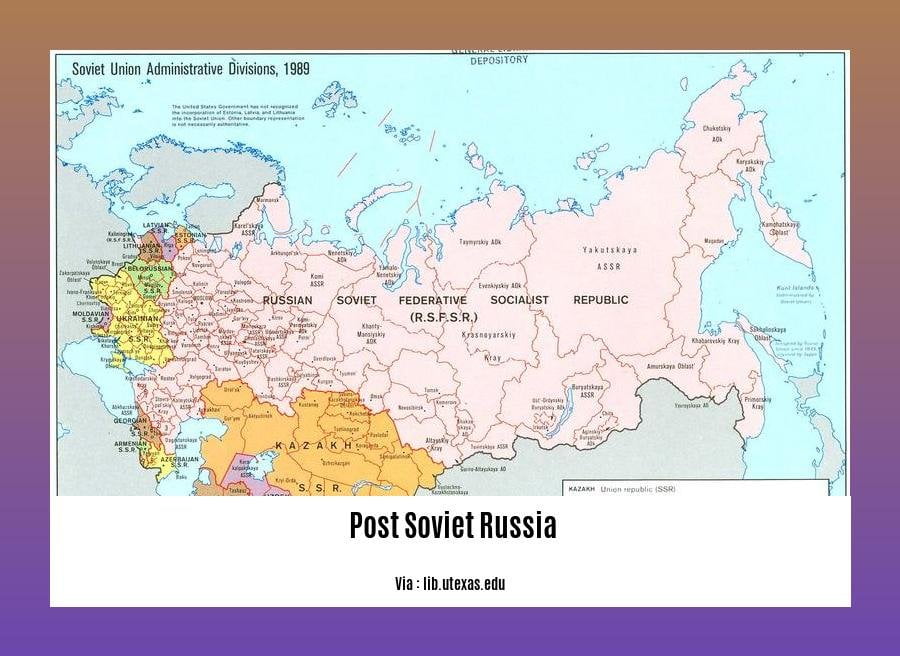
- Russia adopted its Soviet-era constitution and elected Boris Yeltsin as its first president after the collapse of the Soviet Union.
- Russia faced economic collapse due to its inefficient Soviet-era industry and the loss of trade.
- Yeltsin’s economic reforms aimed to address the crisis but led to inflation and poverty.
- Russia experienced political and economic instability during the transition to a market economy.
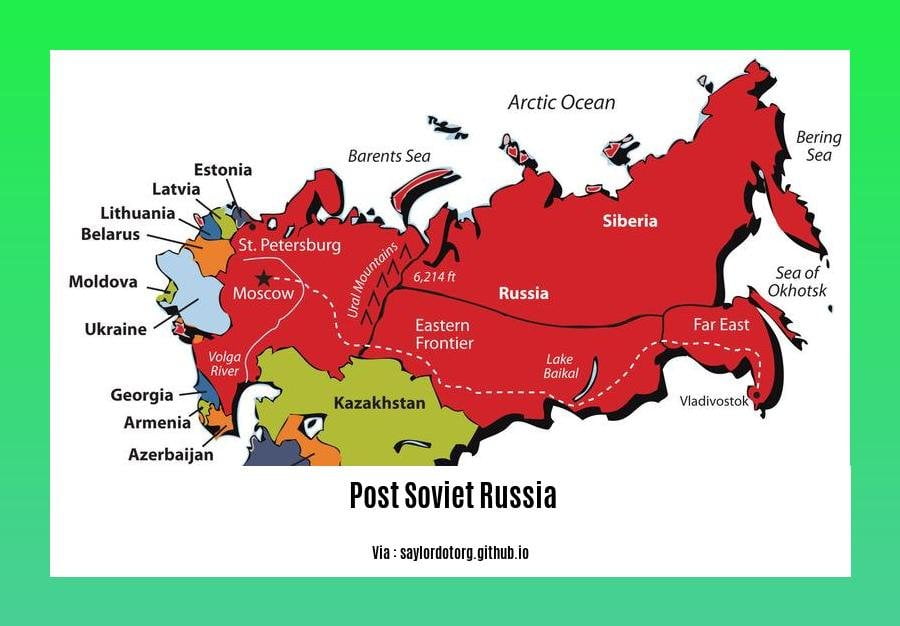
- The Russian Federation is the successor state to the Soviet Union and the largest of the post-Soviet states.
Post-Soviet Russia

In the aftermath of the Soviet Union’s collapse, post-Soviet Russia embarked on a transformative journey. This era has been marked by both challenges and opportunities, shaping the nation’s political, economic, and social landscape.
Economic reforms in the early 1990s, while necessary, led to widespread poverty and inflation. The transition to a market economy was accompanied by political instability, including a failed coup attempt and the Chechen War.
Despite these setbacks, post-Soviet Russia has made strides in building a democratic society and a market-based economy. It has integrated into the global community, joining international organizations like the G20 and the World Trade Organization.
Yet, challenges remain. Post-Soviet Russia continues to grapple with corruption, economic inequality, and geopolitical tensions. It faces the ongoing task of modernizing its economy, diversifying its industries, and strengthening its institutions.
The legacy of the Soviet era continues to shape post-Soviet Russia. The country is still home to a vast nuclear arsenal, a complex federal system, and a strong military. These factors influence its foreign policy and its relationship with the West.
Understanding post-Soviet Russia requires a nuanced understanding of its history, its present-day complexities, and the challenges and opportunities it faces. By delving into its past and present, we can gain insights into the future of this enigmatic nation.
Uncover the fascinating tapestry of Russian history by delving into the history of Russia, tracing its origins from the medieval era to the present day.
Journey through the grandeur of the Tsarist era, witnessing the rise and fall of imperial dynasties that shaped Russia’s destiny.
Explore the pivotal moments that led to the formation of the Soviet Union, understanding its profound impact on global politics and society.
Social Changes and Identity Shifts
Standing at the crossroads of history, post-Soviet Russia has undergone a profound transformation, profoundly impacting its social fabric and individual identities.
Fluidity and Fragmentation
Gone are the days of rigid and monolithic identities. Social Changes and Identity Shifts have become the norm, with individuals fluidly navigating multiple social categories. The concept of self has become less anchored in collective narratives and more open to individual interpretation.
Diversity and Pluralism
The post-Soviet era has given rise to a wide array of social categories, reflecting the diversification of identity systems. Ethnicity, religion, region, and profession have all emerged as salient aspects of self-identification, mirroring the country’s rich cultural and historical tapestry.
From Collectivism to Individualism
The decline of the Soviet collective has led to a shift towards more individualistic orientations. Personal agency and self-expression have gained prominence, as individuals seek to establish their own unique identities within a rapidly changing society.
Nuanced Understanding of the Past
The post-Soviet generation has inherited a complex and often contradictory legacy. Strong dichotomies of the past have given way to a more nuanced understanding of societal realities. Positive and negative evaluations of history have been replaced by a recognition of its intricate tapestry.
Key Takeaways:
- Post-Soviet Social Changes and Identity Shifts have created a fluid and fragmented social landscape.
- The emergence of diverse social categories reflects the country’s cultural and historical richness.
- Individualistic orientations have gained ground, placing greater emphasis on self-expression and personal agency.
- The past is viewed through a nuanced lens, recognizing both its complexities and contradictions.
Sources:
- Multiple Social Identities in the Post-Soviet Context
- Post-Soviet Russian Identity and its Influence on European Security
Foreign Policy and Geopolitical Positioning
As we unravel the complexities of post-Soviet Russia, we dive into the realm of foreign policy and geopolitical positioning. Navigating this intricate landscape requires an understanding of Russia’s aspirations for a multipolar order and its delicate balancing act in the global arena.
Shaping Russian Foreign Policy
Russia’s foreign policy is sculpted by a symphony of factors, including:
- Domestic Regime: The character of the ruling political apparatus.
- International System: The global power dynamics and geopolitical alliances.
- Post-Soviet Space: Russia’s influence and relationships within the former Soviet Republics.
- West-East Relations: The complex interplay with European and Asian nations.
Eurasianism and Westernism
At the heart of Russia’s post-Soviet foreign policy debate lie two contrasting discourses:
- Eurasianism: Emphasizes Russia’s unique civilizational identity and its role in Eurasia.
- Westernism: Advocates for Russia’s integration into the Western world.
Key Takeaways:
- Russia seeks to counter unipolarity and establish a multipolar geopolitical order.
- Russian foreign policy is shaped by a complex interplay of domestic, international, and regional factors.
- The Eurasianist and Westernist discourses continue to influence the contours of Russian foreign policy.
Citations:
- “Russia’s Foreign Policy: Concepts and Approaches” National Center for Biotechnology Information
- “Russian Foreign Policy on the Threshold of the 21st Century” JSTOR
The Legacy of the Soviet Era and its Impact
The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 marked a seismic shift in global politics, leaving a profound [Legacy of the Soviet Era and its Impact] on Russia and the world. The Soviet Union’s dissolution created a power vacuum that reshaped international relations and had far-reaching consequences for Russia’s political, economic, and social fabric.
Political Impact
The end of the Soviet Union ushered in a period of political turmoil and instability in Russia. Boris Yeltsin, the first president of the Russian Federation, led the country through a difficult transition to democracy, grappling with challenges such as economic collapse, ethnic conflicts, and regional separatism. The legacy of the Soviet Union’s authoritarian rule continues to shape Russian politics, with a strong presidency and a centralized government.
Economic Impact
The transition from a centrally planned economy to a market-based system posed significant economic challenges for Russia. Hyperinflation, unemployment, and widespread poverty plagued the country in the 1990s. The legacy of the Soviet Union’s economic policies, such as the emphasis on heavy industry and military production, has had long-lasting effects on Russia’s economic structure.
Social Impact
The demise of the Soviet Union had a profound impact on Russian society. The loss of a shared ideology and the disruption of traditional social structures led to a period of widespread uncertainty and social upheaval. The legacy of the Soviet era continues to influence Russian society, with issues such as social inequality, corruption, and a weakened social safety net remaining significant challenges.
Key Takeaways:
- The collapse of the Soviet Union created a power vacuum that reshaped international relations.
- Russia faced significant political instability and economic challenges during the transition to democracy.
- The legacy of the Soviet era continues to shape Russian politics, economics, and society.
Sources:
- Russia – Post-Soviet Russia
- The Birth of the Soviet Union and the Death of the USSR
FAQ
Q1: What were the major challenges faced by Russia after the collapse of the Soviet Union?
Q2: How did Boris Yeltsin contribute to Russian history?
Q3: What is the significance of the post-Soviet foreign policy debate in Russia?
Q4: What is the role of the Russian Federation in the post-Soviet space?
Q5: How did Russia’s economic reforms impact the country in the early 1990s?
- Unlocking Francis Alexander Shields’ Finance Empire: A Comprehensive Biography - July 12, 2025
- Unveiling Francis Alexander Shields: A Business Legacy - July 12, 2025
- Francis Alexander Shields’ Business Career: A Comprehensive Overview - July 12, 2025