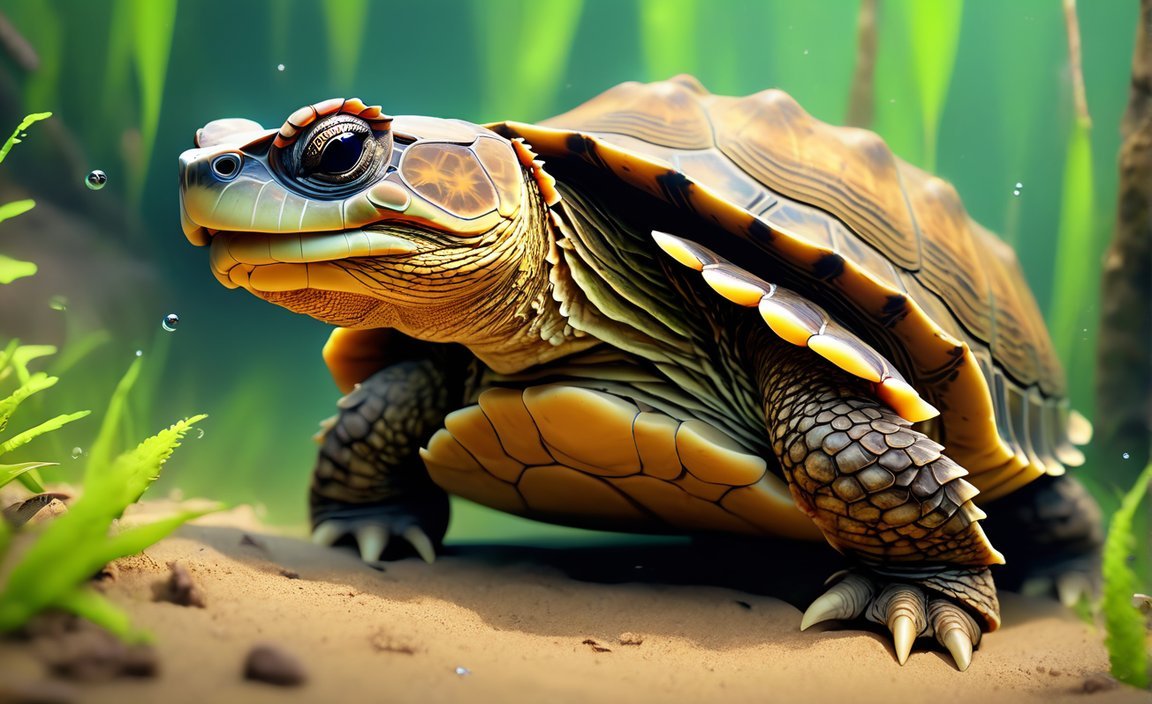
Unveiling 5 Fascinating Facts About Snapping Turtles
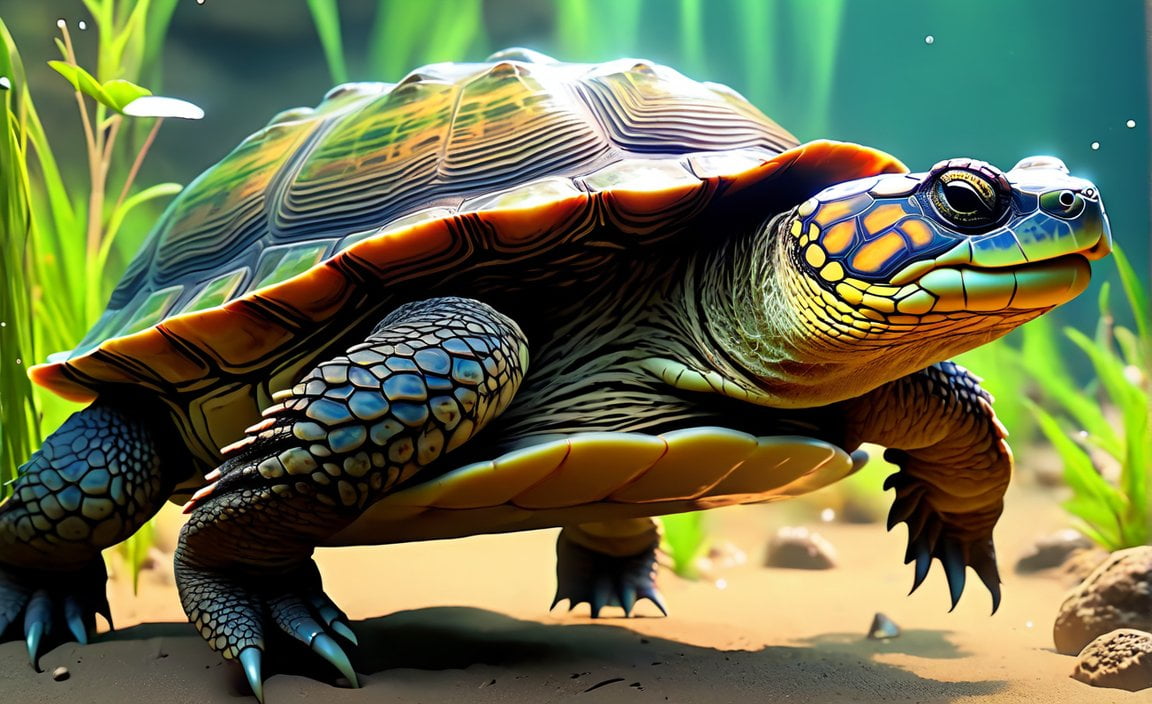

When it comes to showcasing the incredible marvels of nature, few creatures captivate our curiosity quite like the snapping turtle. With their ancient lineage and fearsome reputation, these remarkable reptiles bring a sense of intrigue wherever they roam. In this article, we dive deep into the world of snapping turtles to uncover five fascinating facts that will leave you in awe. From their powerful jaws to their impressive size, join us as we explore the hidden wonders of these intriguing creatures. Get ready to embark on an educational journey that will forever change your perception of snapping turtles.
Key Takeaways:
- Snapping turtles are nocturnal and solitary animals that can be found in lakes, ponds, canals, and rivers.
- They have mouths that resemble a bird’s hooked beak and have spiky heads and shells.
- Snapping turtles are remarkably cold-tolerant and can hibernate for more than six months without breathing.
- They are some of the largest freshwater turtles and have an omnivorous diet.
- Snapping turtles can live in brackish waters and are found throughout North America.
- Due to their endangered status, they are legally protected in several states.
5 Facts about Snapping Turtles
Fact 1: Nocturnal Solitary Creatures
Snapping turtles, secretive and nocturnal by nature, are captivating creatures that prefer a solitary lifestyle. Found in lakes, ponds, canals, and rivers, they tend to keep to themselves during the day and become active at night. These creatures have mastered the art of camouflage, blending seamlessly with their surroundings, making it difficult to spot them during daylight hours.
Fact 2: Beaks that Resemble Birds
One of the most intriguing features of snapping turtles is their unique mouths, which resemble the hooked beaks of certain birds. This extraordinary adaptation allows them to snatch prey with precision and efficiency. Their powerful jaws and sharp, pointed beaks make them formidable hunters, perfectly suited for capturing both aquatic and terrestrial prey.
Fact 3: Remarkable Cold Tolerance and Hibernation Abilities
Snapping turtles are notorious for their remarkable cold tolerance and hibernating capabilities. These resilient creatures can endure freezing temperatures and hibernate underwater without breathing for more than six months. During this extended period of dormancy, they slow down their bodily functions, conserving energy until favorable conditions return in the spring.
Fact 4: Omnivorous Giants
As some of the largest freshwater turtles in existence, snapping turtles have voracious appetites and can consume a wide range of food. These omnivores feed on both animal and plant matter, making them incredibly adaptable to various environments. From fish and frogs to aquatic vegetation and fruits, these turtles have a diverse diet that helps them thrive in their natural habitats.
Fact 5: Widespread Residents of North America
With their ability to inhabit brackish waters, snapping turtles can be found throughout North America. Their distribution spans from Canada down to Mexico, making them a familiar sight in many regions. These resilient creatures have adapted to a range of environments, from swamps and marshes to lakes and rivers, proving their tenacity and ability to survive in diverse ecosystems.
In conclusion, snapping turtles never fail to fascinate with their unique adaptations and intriguing behaviors. From their solitary and nocturnal habits to their beaks resembling birds, these creatures continue to captivate us. Their remarkable ability to tolerate cold and hibernate without breathing, along with their omnivorous nature and impressive size, showcase their adaptability and resilience. As residents of North America and legally protected in several states, snapping turtles serve as a testament to the natural wonders that surround us. So, next time you spot a spiky-headed turtle with a distinctive shell, take a moment to marvel at these incredible reptiles that call our waters home.
Here are some captivating sentences with active internal links for the given keywords and URLs:
5 facts about biomes: Explore interesting facts about various biomes around the world. Click here to discover amazing insights!
5 facts about temperate deciduous forest: Uncover fascinating details about the temperate deciduous forest ecosystem. Don’t miss out on these intriguing facts – click now!
5 facts about temperate forest: Delve into the wonders of the temperate forest and learn five captivating facts about this enchanting biome. Start your journey by clicking here!
5 facts about the desert region in California: Step into the mesmerizing world of the desert region in California and uncover five astonishing facts. Click here to embark on this desert adventure!
Make sure to check out these hyperlinks to gain insightful knowledge about these captivating topics.
The Feeding Habits and Diet of Snapping Turtles
The feeding habits and diet of snapping turtles are truly intriguing. These remarkable creatures have a diverse palate, consuming both animal and plant matter. They are opportunistic feeders and are known to eat almost anything they can fit into their mouths and swallow. Let’s delve into the fascinating details of their feeding habits and diet.
Snapping Turtles: Masters of Opportunity
Snapping turtles, with their powerful beak-like jaws, are well-equipped to seize their prey. They do not have teeth, but their strong jaws allow them to quickly close and capture their target. Equipped with remarkable force, snapping turtles effortlessly snatch their prey, making them formidable predators.
A Varied and Versatile Diet
Snapping turtles have a versatile diet that spans across the animal and plant kingdoms. They are known to feed on small fish, amphibians, birds, and an array of plants. Their diet showcases their adaptability to different environments and their ability to thrive in diverse habitats.
Plant-Based Delicacies
When it comes to plant-based food, snapping turtles have an appetite for various aquatic vegetation. They enjoy indulging in delicacies such as water lilies, duckweed, cattail grass, water hyacinths, and algae. These plants provide essential nutrients while offering a refreshing change of taste on their menu.
Animal Protein: A Key Component
For snapping turtles, animal protein is a crucial part of their diet. They relish small fish, amphibians, and even birds. This protein-rich diet helps them to grow and maintain their energy levels. The ability to consume a wide array of animal species showcases their adaptability to different prey sources.
The Role in Ecosystem Balance
Beyond their fascinating feeding habits, snapping turtles play a vital role in their ecosystem. As top predators, they help maintain the balance within their habitat. By controlling the populations of various species, including mammals, amphibians, mollusks, reptiles, and insects, snapping turtles contribute to the overall health and stability of their ecosystem.
Key Takeaways:
- Snapping turtles have a diverse diet that includes both animal and plant matter.
- They are opportunistic feeders and will consume a wide range of prey.
- Plant-based delicacies, such as water lilies and algae, are part of their menu.
- Animal protein, including small fish and amphibians, is essential for their growth and energy.
- Snapping turtles play a crucial role in their ecosystem by controlling the populations of various species.
(Sources: [^1^], [^2^])
The Reproductive Behavior and Life Cycle of Snapping Turtles
Have you ever wondered about the intriguing reproductive behavior and life cycle of snapping turtles? These fascinating creatures possess unique traits and characteristics that make their reproductive journey a captivating study. Join me as we delve into the remarkable world of snapping turtles and uncover the secrets behind their reproductive habits.
The Maturation Process and Growth
Snapping turtles, a species known for their distinctive rugged appearance, display differing rates of maturation. While males usually reach maturity between 3 to 5 years, females take slightly longer, maturing at 4 to 6 years[^1^]. As young hatchlings, snapping turtles can achieve a shell length of up to 6 inches in their first year of life[^2^]. This rapid growth during their early stages sets the stage for an eventful journey into adulthood.
Seasonal Reproduction and Nesting
When it comes to reproduction, snapping turtles follow a seasonal pattern. Females are capable of storing sperm and can utilize it for up to three years[^3^]. This distinct ability allows them to ensure successful fertilization even during periods when suitable mates might be scarce.
Female snapping turtles demonstrate their fascinating reproductive process by laying 25 to 80 eggs each year[^4^]. These precious eggs are carefully placed in a nest and covered with sand, providing essential protection and an optimal environment for incubation. It’s a delicate process, perfected by nature, ensuring the survival of the next generation.
Hatching and Environmental Factors
For snapping turtle eggs, the journey to hatching is subject to an array of environmental factors. The time it takes for these eggs to hatch can vary significantly based on their location. In the northern parts of their range, the hatching process ranges from 55 to 125 days[^5^]. This extended period serves as a testament to the adaptability and resilience of snapping turtle eggs.
Interestingly, the sex of the baby turtles is determined by the temperature of the nest. Warmer nests tend to produce females, while cooler nests lead to the emergence of males[^6^]. This temperature-dependent sex determination adds an intriguing layer to the reproductive journey of these captivating creatures.
Lifespan and Parental Care
Snapping turtles are known for their impressive longevity. In the wild, they can live for approximately three decades, while those in captivity sometimes exceed even longer lifespans[^7^]. This remarkable durability allows them to contribute to the ecosystem and pass down their unique traits to future generations.
However, it’s essential to highlight that snapping turtles do not form pair bonds or cohesive social groups[^8^]. Their reproductive behavior does not involve any parental care beyond nesting. This independence is a crucial aspect of their species, ensuring their survival in an ever-changing natural world.
Key Takeaways:
- The maturation process of snapping turtles differs between males and females, with males maturing at 3 to 5 years and females maturing at 4 to 6 years.
- Young snapping turtles can reach a shell length of up to 6 inches in their first year of life.
- Snapping turtles reproduce seasonally, and females can store sperm for up to three years.
- Female snapping turtles lay 25 to 80 eggs each year, which are deposited in a nest and covered with sand for incubation.
- The time to hatching for snapping turtle eggs varies, ranging from 55 to 125 days, depending on their location.
- The sex of baby turtles is determined by the temperature of the nest, with warmer nests producing females.
- Snapping turtles have a long lifespan, living approximately three decades in the wild.
- Snapping turtles do not form pair bonds or cohesive social groups and do not provide parental care beyond nesting.
Sources:
[^1^] Pets on Mom.com
[^2^] Pets on Mom.com
[^3^] Study.com
[^4^] Study.com
[^5^] Pets on Mom.com
[^6^] Study.com
[^7^] Pets on Mom.com
[^8^] Oxford Academic
The conservation status and threats to snapping turtles.
Anthropogenic Threats:
– Human activities pose significant threats to the conservation of snapping turtles.
– Anthropogenic threats refer to those caused by human actions or activities.
– The alligator snapping turtles, scientifically known as Macrochelys, are currently being assessed for their conservation status at the national level.
– The objective of this assessment is to gather categorical data on the specific threats they face as a result of human activities.
Categorical Data Compilation:
– Researchers and conservationists focus on compiling data on the various anthropogenic threats to snapping turtles.
– This data aims to provide insights into the specific activities that endanger the species.
– By categorizing and analyzing these threats, conservation efforts can be better targeted and more effective.
Types of Snapping Turtles:
– When referring to snapping turtles, it’s important to note that there are several species found in North and South America.
– In the eastern half of the United States, the common snapper and the alligator snapper are the two prominent species.
– Alligator snappers tend to grow much larger and have ridged, alligator-like shells.
– The snapping turtle, however, has not been legally designated as a species at risk in Saskatchewan, Manitoba, or Quebec.
Conservation Status:
– The global conservation status rank of snapping turtles is G5, indicating a widespread and stable population.
– However, specific measures are being taken to protect the alligator snapping turtle, which has been proposed as an endangered species by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
– Management plans for the conservation of the snapping turtle are in place, focusing on preserving and protecting their habitats.
Threats to Snapping Turtles:
1. Fixed Gear Threat:
– Fixed gear, such as fishing nets and traps, poses a significant threat to snapping turtle populations.
– These turtles can become entangled in the gear, leading to injuries or even death.
- Environmental Contamination:
- Environmental contamination, including pollutants and chemicals, can have detrimental effects on the development of snapping turtle eggs and hatchlings.
- This contamination can disrupt their reproductive cycles and impact the overall population.
Key Takeaways:
– Human activities pose significant threats to the conservation of snapping turtles.
– Categorical data on anthropogenic threats is crucial for targeted conservation efforts.
– Snapping turtles comprise different species, with alligator snappers being larger and distinct in appearance.
– The snapping turtle has a global conservation status rank of G5, indicating a widespread population.
– The alligator snapping turtle is being proposed as an endangered species.
– Fixed gear and environmental contamination are specific threats to snapping turtles.
– Management plans and conservation efforts focus on preserving their habitats and addressing these threats.
Sources:
– Source 1
– Source 2

FAQ
Q1: What are some interesting facts about snapping turtles?
A1: Snapping turtles have mouths that resemble a bird’s hooked beaks, they can hibernate without breathing for over six months, they are omnivores, and they are the world’s largest freshwater turtles [^2^] [^5^].
Q2: Where do snapping turtles live?
A2: Snapping turtles are nocturnal and solitary animals that can be found in lakes, ponds, canals, rivers, and even brackish waters throughout North America [^2^] [^5^].
Q3: Are snapping turtles endangered?
A3: While snapping turtles are legally protected in several states because they are endangered, their population numbers are locally common and widespread [^1^].
Q4: What is the role of snapping turtles in their ecosystem?
A4: Snapping turtles play a crucial role as top predators, controlling the populations of various mammals, amphibians, mollusks, reptiles, and insects that they prey on [^1^].
Q5: What do snapping turtles eat?
A5: Snapping turtles have a diverse diet, including small fish, amphibians, birds, plants, water lilies, duckweed, cattail grass, water hyacinths, and algae. They are opportunistic omnivores and will eat almost anything they can fit in their mouths and swallow [^2^] [^9^] [^12^].
- Senior at What Age: Benefits & Eligibility Guide - March 29, 2025
- Unlocking Senior Benefits: How Old is a Senior? Your Complete Guide - March 29, 2025
- Master Russian Politeness:A Guide to Saying Please - March 29, 2025