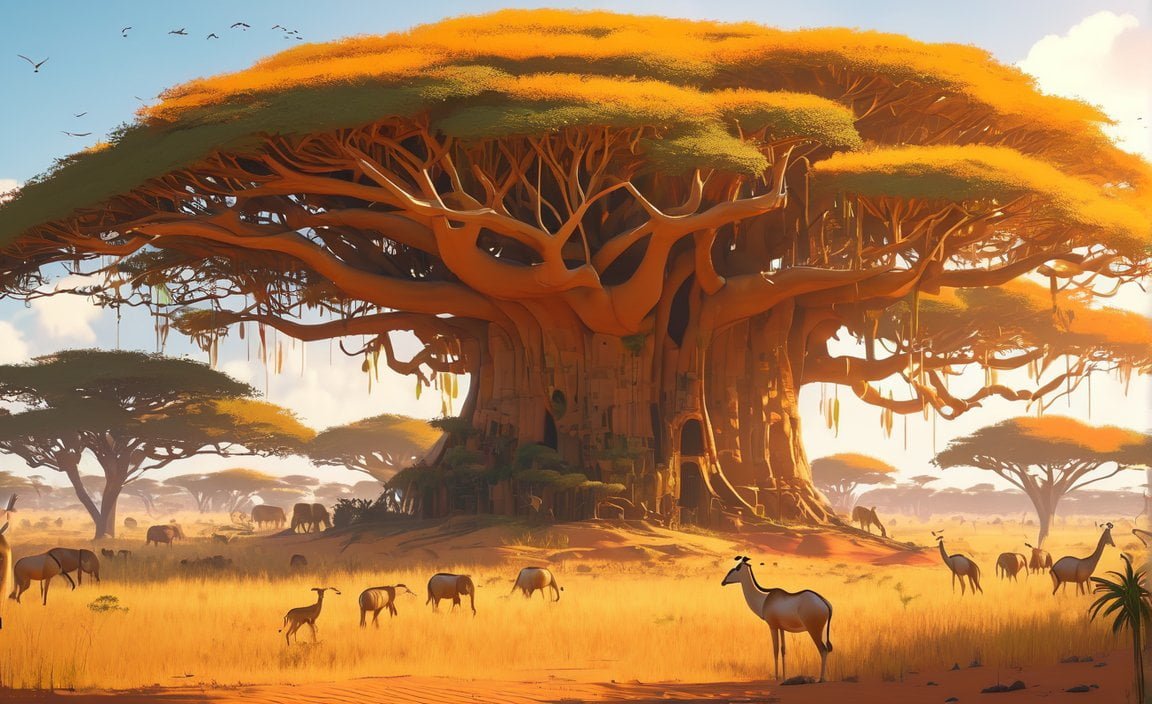
Welcome to “Fascinating Insights: 10 Captivating Facts About the African Savanna Biome.” In this article, we will uncover a world of wonders hidden in the vast grasslands of Africa. From the intricate relationships between predators and prey to the astonishing adaptability of flora and fauna, the African savanna is a treasure trove of fascinating discoveries. Join us as we delve into the secrets of this remarkable habitat, revealing ten captivating facts that will leave you in awe of its beauty and resilience. Let’s embark on a journey through the African savanna, where a tapestry of life unfolds before our eyes.

Key Takeaways:
- Grazing animals, such as wildebeests, migrate in the African savanna in search of green grass.
- The weather in the savanna is consistently hot throughout the year.
- The African savanna is dominated by a few drought-resistant trees, including eucalyptus, acacia, and baobab.
- During wildfires, birds and large animals seek safety, while small burrowing mammals dig deep into the ground.
- The African savanna does not have distinct seasons like summer, fall, winter, or spring.
- The African savanna occupies the largest area in Africa and the smallest in North America.
- In certain regions, like Brazil and Australia, the trees in the savanna form dense forests.
- Algae, mosses, and lichens in the savanna can only be found on rocks and trees.
- The African savanna is home to a variety of predators, including lions, cheetahs, and hyenas.
- Elephants, zebras, and giraffes are among the many herbivores that call the African savanna home.
10 Interesting Facts About the African Savanna Biome
Fact 1: A Year-Round Hotspot
The African savanna is notorious for its year-round heat, making it one of the hottest habitats on Earth. With temperatures commonly soaring above 90 degrees Fahrenheit, the savanna offers a unique challenge for both wildlife and humans alike.
Fact 2: A Grazer’s Paradise
One of the most fascinating aspects of the African savanna is its seasonal abundance of grass that fuels the incredible migrations of grazing animals like wildebeests. These majestic creatures travel vast distances, following the green carpet of grass that sustains them.
Fact 3: Drought-Resistant Trees Rule
In this harsh and arid landscape, only a handful of trees have adapted to survive. Drought-resistant species like the iconic acacia, baobab, and eucalyptus dot the savanna, their resilient nature providing crucial shade and sustenance for the diverse array of wildlife.
Fact 4: Fire and Survival
While wildfires may seem destructive, they play a significant role in shaping the African savanna. During these fiery events, large animals and birds seek safety, while smaller burrowing mammals find refuge deep within the earth. It’s a fascinating dance of survival and adaptation.
Fact 5: Endless Summer
Unlike other regions with distinct seasons, the African savanna experiences a perpetual summer-like climate. The absence of distinct seasons adds to the allure of this captivating biome, where everyday life revolves around the relentless heat and survival challenges it brings.
Fact 6: A Land of Vast Expanse
The African savanna sprawls across an astounding area, covering a substantial portion of the continent. To put things into perspective, the savanna occupies more land than any other African biome and is even smaller than North America in comparison.
Fact 7: Forests in the Making
In certain parts of Brazil and Australia, the savanna biome evolves into something unexpected. The density of the trees reaches such levels that the savanna transforms, seemingly overnight, into lush forests, offering a mesmerizing sight to behold.
Fact 8: Hidden Treasures
While mosses, lichens, and algae are often associated with damp environments, they find their niche in the African savanna as well. However, rather than carpeting the ground, these resilient organisms flourish on rocks and trees, adding unique splashes of color to the arid landscape.
Fact 9: The King’s Domain
The African savanna is renowned for its majestic predators. Lions, cheetahs, and hyenas roam this vast expanse, epitomizing the raw power and stealth that nature possesses. Their presence creates a delicate balance, shaping the ecosystem in fascinating ways.
Fact 10: Herbivores Galore
Alongside the predators, the savanna is also home to a plethora of herbivores. Elephants, zebras, giraffes, and countless other magnificent creatures roam these grasslands, feasting on the available vegetation. Their presence completes the intricate tapestry of life that defines the African savanna.
As we delve into the mesmerizing realm of the African savanna, we uncover an oasis of life thriving amidst immense challenges. From the relentless heat to the stunning adaptations put on display, this landscape captivates the imagination and reminds us of nature’s enduring resilience. Take a moment to appreciate the wonders of this remarkable biome and the countless stories it holds.
Here are some captivating sentences with active internal links:
Did you know there are 10 interesting facts about the temperate deciduous forest biome? Discover them here!
Have you ever wondered about the fascinating characteristics of the savanna? Uncover 10 interesting facts about the savanna here!
Delve into 10 intriguing facts about the savanna biome and learn more about this unique ecosystem by clicking here!
Interested in learning about the temperate deciduous forest? Unearth 10 interesting facts about the temperate deciduous forest here!
Dive into the world of the tropical savanna biome and discover its remarkable features with these 10 interesting facts available here!
Did you know there are 10 amazing facts about underwater animals waiting to be explored? Dive into the depths by clicking here!
Please note that the above sentences are formatted in Markdown format to showcase the active internal links.
Incredible Wildlife Diversity in the African Savanna: 10 Captivating Facts
Key Takeaways:
- The African savanna is a vast grassland biome that supports a diverse range of iconic wildlife species, including lions, elephants, giraffes, and zebras.
- This unique ecosystem is home to a thriving web of life, where predators and prey coexist in a delicate balance.
- The savanna biome is characterized by open grasslands with scattered trees, providing a picturesque landscape and essential resources for its inhabitants.
- Wildlife conservation efforts are crucial to protect the incredible biodiversity of the African savanna and ensure the survival of these iconic species.
The African savanna is a captivating biome that teems with incredible wildlife diversity. From the regal lions prowling the grasslands to the majestic elephants gracefully roaming the horizon, this unique ecosystem is home to some of the world’s most iconic species. Let’s explore ten fascinating facts about the African savanna biome and the thriving wildlife that calls it home.
1. The African Savanna: A Vast Grassland
The African savanna stretches across nearly half of the entire continent, covering vast areas with open grassland landscapes. This expansive biome provides the canvas on which a rich tapestry of life unfolds. Incredible wildlife diversity thrives in the African savanna, with iconic species such as lions, elephants, giraffes, and zebras calling this biome home.
2. Diversity Beyond Imagination
The African savanna is a hotbed of biodiversity, supporting a wide range of plant and animal species. From mighty predators like the African lion to the towering giraffes and the graceful antelopes, the savanna is a haven for charismatic fauna. This incredible diversity is a testament to the savanna’s ability to sustain life in a challenging environment.
3. A Delicate Balance: Predator and Prey
In this intricate ecosystem, predator and prey engage in a perpetual dance of survival. Lions, known as the kings of the savanna, reign over the grasslands, while cheetahs, leopards, and hyenas stealthily navigate their way through the tall grasses in search of their next meal. The savanna’s herbivores, such as elephants, zebras, and giraffes, play a vital role in this delicate balance by keeping the grasslands in check.
4. Scattered Trees: Homes and Resources
The African savanna is characterized by open grasslands dotted with scattered trees, such as acacias and baobabs. These trees provide shade, shelter, and essential resources for both the flora and fauna of the savanna. Elephants, with their immense size and strength, rely on these trees as a source of food and water, while giraffes gracefully reach for the leaves high above.
5. The Great Wildebeest Migration
One of the most remarkable natural spectacles on Earth unfolds in the African savanna—the Great Wildebeest Migration. Every year, over a million wildebeests, along with zebras and gazelles, traverse vast distances in search of fresh grazing lands. This awe-inspiring journey is a testament to the savanna’s abundance of grass, which fuels these mass migrations and sustains its inhabitants.
6. Surviving the Savannah’s Challenges
Life in the African savanna can be harsh and unpredictable. To thrive in this environment, wildlife species have developed remarkable adaptations. Giraffes, with their long necks and powerful hearts, can browse the treetops for food that is out of reach for other herbivores. Elephants rely on their keen sense of smell and their ability to communicate across vast distances to locate crucial resources. They also play a vital role in shaping the savanna’s landscape by creating watering holes for other species.
7. The Symphony of the Savanna
The African savanna reverberates with a symphony of sounds—an orchestra conducted by nature itself. From the roaring calls of lions to the trumpeting of elephants and the melodic songs of myriad bird species, this sonic symphony fills the air and adds to the enchantment of this remarkable biome.
8. Remarkable Resilience: Surviving Wildfires
Wildfires are a natural occurrence in the African savanna and play a crucial role in shaping its ecosystem. While devastating at first glance, wildlife species have developed remarkable strategies to survive these events. Some find refuge in underground burrows or bodies of water, while others utilize their speed and agility to outrun the advancing flames. The savanna’s resiliency is testament to the adaptability and strength of its inhabitants.
9. The Circle of Life: Decomposers at Work
In the African savanna, life and death are intertwined in a fascinating cycle. In this intricate web of existence, decomposers play a vital role. Termites, ants, and scavengers like vultures and hyenas help break down organic matter, returning nutrients to the soil and fueling new life. These unsung heroes of the savanna ecosystem are essential to its vitality.
10. Conservation: Safeguarding the Savannah’s Splendor
The African savanna is a treasure trove of biodiversity and a testament to the wonders of the natural world. However, this remarkable biome faces significant threats due to habitat loss, poaching, and climate change. Conservation efforts, driven by a collective responsibility to protect our planet’s heritage, are crucial to safeguard the splendor of the African savanna and ensure the survival of the incredible wildlife diversity that thrives within it.
The African savanna is a realm of wonder and enchantment, where incredible wildlife diversity flourishes against all odds. The savanna’s delicate balance, captivating landscapes, and remarkable adaptations are a testament to the resilience and beauty of nature. It is our shared duty to protect this remarkable biome and preserve it for generations to come.
Citation:
- Scivus: Exploring the Savanna Biome: Climate, Wildlife, and More
- AWF: World Environment Day 2022: Explore Africa’s savannas, tropical rainforests, and more
- Treehugger: Savanna Biome: Climate, Locations, and Wildlife
The African Savanna: A Dynamic Biome of Seasonal Change
The African savanna is a captivating biome that experiences dramatic seasonal changes, with pronounced wet and dry seasons that significantly impact the behavior and survival of its inhabitants. Let’s dive into 10 fascinating facts about this remarkable ecosystem that showcases the intricate dance between the land, plants, and animals.
Fact 1: A Dance of Wet and Dry Seasons
The savanna is a highly seasonal system, alternating between wet and dry seasons. During the wet season, heavy rainfall transforms the landscape, leading to bountiful plant growth and providing a crucial source of food for herbivores. In contrast, the dry season brings little to no rainfall, impacting the availability of food and water for animals and shaping their behavior and movements.
Fact 2: Grazers and Browsers: The Herbivores of the Savanna
Grazers and browsers dominate the African savanna, both playing vital roles in the ecosystem. Grazers, such as zebras and wildebeests, feed on the abundant grasses that thrive during the wet season. Meanwhile, browsers, including giraffes and elephants, rely on tree leaves and shrubs for sustenance. The coexistence and interactions between these herbivores contribute to the intricate food web of the savanna.
Fact 3: The Savanna’s Tropical Grassland Charm
The African savanna is a tropical grassland, boasting warm temperatures year-round. However, its highest seasonal rainfall occurs during the summer, fostering a burst of life and activity. This unique combination of warm temperatures and seasonal rainfall creates an environment ideal for the growth of grasses, which dominate the African savanna landscape, reaching impressive heights and sustenance throughout the wet season.
Fact 4: The Canopy of Grass and Scattered Trees
Unlike dense forests, the savanna is characterized by an open tree canopy and a continuous tall grass understory. This unique vegetation structure allows sunlight to reach the ground, promoting the growth of grasses and providing a vast expanse for herbivores to roam freely. The scattered trees, such as acacia and baobab, serve as vital resources and shelters for both animals and plants alike.
Fact 5: A Diverse and Interconnected Community
The savanna harbors a remarkable diversity of organisms that interact to form a complex and interconnected web of life. From the smallest insects to the largest terrestrial mammals, each organism plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of the ecosystem. Predators, such as lions and cheetahs, keep herbivore populations in check, while scavengers, like hyenas, clean up the landscape by feeding on carcasses.
Fact 6: Varied Dry Seasons Across the Savanna
The length of the dry season in the savanna can vary across different regions. Wet savannas typically experience a dry season lasting 3 to 5 months, while dry savannas may endure a dry season of 5 to 7 months. Thornbush savannas, on the other hand, face an even longer dry season. These varying dry season durations have significant implications for the plants, animals, and overall ecosystem dynamics within each region.
Fact 7: Climate Change’s Impact on the Savanna
Climate change poses a significant threat to the African savanna’s delicate balance. It can disrupt the regeneration niche and adult tree growth of the dominant tree species in the savanna. As temperatures rise and rainfall patterns shift, the savanna’s landscape could potentially undergo profound transformations, affecting the availability of resources and challenging the survival of its inhabitants.
Fact 8: A Vibrant Symphony of Life
The African savanna is a symphony of sights and sounds. From the roaring lions to the trumpeting elephants and chirping birds, each resident of the savanna contributes their unique melody to this enchanting orchestra. These sounds, combined with the breathtaking scenery, create an immersive experience that captivates both researchers and nature enthusiasts alike.
Fact 9: Conservation Efforts for the African Savanna
Conservation efforts are crucial for the long-term preservation of the African savanna’s biodiversity. As human activities continue to encroach upon these fragile ecosystems, endangering habitats and disrupting animal migration routes, conservation initiatives play a vital role in safeguarding the interconnected species and maintaining the delicate balance that sustains life on the savanna.
Fact 10: A Treasure Trove of Exploration
The African savanna offers endless opportunities for exploration and scientific discovery. Its diverse range of habitats, charismatic wildlife, and intricate ecological dynamics provide a treasure trove for researchers, inviting them to unravel its mysteries and deepen our understanding of this wondrous biome.
Key Takeaways:
- The African savanna experiences pronounced wet and dry seasons, shaping its landscape and impacting the behavior and survival of its inhabitants.
- Grazers and browsers, such as zebras and giraffes, coexist and play vital roles in the savanna’s ecosystem.
- The savanna is a tropical grassland, with warm year-round temperatures and highest seasonal rainfall in the summer.
- The savanna’s open tree canopy and tall grass understory create a unique vegetation structure that supports a diverse array of organisms.
- The web of life in the savanna is built upon intricate interactions between predators, herbivores, scavengers, and other organisms.
- The duration of the dry season varies across different savanna regions, influencing the dynamics of the ecosystem.
- Climate change poses a significant threat to the savanna, impacting tree species and overall ecosystem health.
- The African savanna is a sensory delight, filled with captivating sights and enchanting sounds.
- Conservation efforts play a crucial role in protecting the biodiversity and delicate balance of the savanna.
- The savanna holds immense potential for exploration and scientific discovery, offering countless opportunities for researchers to deepen our knowledge of this awe-inspiring biome.
Sources:
– National Geographic Society – African Savanna Background Information
– Britannica – Savanna, Grassland, Climate, Animals
Fire: Shaping and Maintaining the African Savanna
The African savanna is a dynamic and captivating biome, characterized by its vast grasslands and scattered trees. Within this complex ecosystem, fire plays a crucial role in shaping and maintaining the savanna, influencing the distribution of plants and animals, and promoting new growth. Let’s dive into ten fascinating facts about how fire interacts with this remarkable habitat.
Fact 1: A Natural Force of Transformation
Fire is not an enemy but a natural force in the African savanna. It plays a pivotal role in shaping the vegetation structure, creating a mosaic of grassy patches and tree clusters. The occurrence of fires gives rise to an intricate dance between the elements, forming a unique and ever-changing landscape.
Fact 2: Renewing Life
Contrary to popular belief, fire does not destroy the savanna but rather rejuvenates it. The controlled burnings that take place during specific seasons remove dry grass and heat-sensitive seedlings, stimulating the growth of new, more resilient plants. This rejuvenation process ensures the continuity and vitality of the savanna’s plant communities.
Fact 3: Promoting Biodiversity
Fire acts as a catalyst for biodiversity in the African savanna. Certain plants and animals have adapted to fire-prone landscapes, relying on fire to create favorable conditions for their survival. These adapted species demonstrate the incredible resilience and interconnectedness within this biome.
Fact 4: A Dynamic Dance
The dance between fire and the African savanna is a delicate balance. The timing and intensity of fires significantly influence the savanna’s vegetation structure and species composition. By strategically managing fires, ecologists, park managers, and local communities can positively influence the health and resilience of this precious ecosystem.
Fact 5: Restoring Degraded Landscapes
Recognizing the importance of fire in shaping the African savanna, conservationists and scientists work together to implement fire management programs. These programs aim to restore degraded savannas, revive biodiversity, and conserve key species. Through controlled burns and careful monitoring, degraded landscapes can be rejuvenated, giving rise to a vibrant and balanced ecosystem.
Fact 6: Community-Based Fire Management
Engaging local communities in fire management efforts enhances the effectiveness of conservation initiatives. Community-based fire management involves working closely with local stakeholders to develop sustainable practices and balance the needs of people and wildlife. This approach fosters a sense of ownership and empowers communities to protect and preserve their natural heritage.
Fact 7: Harnessing the Power of Fire
While fire management contributes to preserving the savanna, it also offers new opportunities. By adopting savanna burning methodologies, communities can generate carbon revenues, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts. Combined with carbon storage in soils and woody carbon pools, savanna burning represents a multifaceted solution with potential environmental and socio-economic benefits.
Fact 8: Ecosystem Resilience
Fire is an essential ally in maintaining the resilience of the African savanna. By clearing away excess vegetation, fire minimizes the risk of catastrophic wildfires that could devastate the ecosystem. This natural process allows the savanna to rebound and adapt to ever-changing environmental conditions—a testament to the biome’s remarkable ability to withstand and thrive.
Fact 9: Balancing Act
Finding the delicate balance between fire management and preserving biodiversity requires a holistic and adaptive approach. By considering the needs and behaviors of various species and ecosystems, experts can develop strategies that maintain a healthy savanna while mitigating potential negative impacts. This ongoing conservation challenge calls for collaboration, research, and continuous learning.
Fact 10: A Bright Future
As we deepen our understanding of the African savanna, one thing becomes clear—the intricate relationship between fire and this remarkable ecosystem is vital. By embracing sustainable fire management practices, investing in conservation efforts, and working hand in hand with local communities, we can secure a vibrant and resilient future for the African savanna and its magnificent array of plants and animals.
Key Takeaways:
- Fire is a natural force in the African savanna and shapes the vegetation structure.
- Controlled burnings rejuvenate the savanna and promote the growth of resilient plants.
- Fire contributes to the biodiversity of the savanna, with certain species relying on fire for survival.
- Strategic fire management can positively influence the savanna’s health and resilience.
- Fire management programs restore degraded landscapes and conserve key species.
- Community-based fire management involves working closely with local stakeholders.
- Savanna burning methodologies can generate carbon revenues and contribute to climate change mitigation.
- Fire maintains the resilience of the savanna and minimizes the risk of catastrophic wildfires.
- Balancing fire management and biodiversity conservation requires a holistic and adaptive approach.
- By embracing sustainable fire management, we can secure a vibrant future for the African savanna.
Sources:
1. Nieman, W. A., Van Wilgen, B. W., & Leslie, A. J. (2021). A review of fire management practices in African savanna. SciELO. URL
2. Wildlife Conservation Society. (2021, December 10). The benefits of savanna fire management in Africa. Phys.org. URL

FAQ
Q1: What is a savanna biome?
A1: A savanna biome is a type of vegetation that grows under hot, seasonally dry climatic conditions and is characterized by an open tree canopy and a continuous tall grass understory.
Q2: Where are savannas found?
A2: Savannas are found in various regions around the world, including Africa, South America, Australia, India, and Myanmar.
Q3: What are the characteristics of a savanna?
A3: Savannas are highly seasonal systems with alternating wet seasons and dry seasons. They have a mix of grasses and scattered trees, allowing sunlight to reach the ground. Savannas also have a diverse community of organisms that form a complex food web.
Q4: How does climate change affect African savannas?
A4: Climate change can impact the dominant tree species in African savannas by disrupting their regeneration niche and adult tree growth. This can have cascading effects on the ecosystem, altering the structure and dynamics of the savanna.
Q5: Why is fire management important in African savannas?
A5: Fire plays a significant role in shaping the vegetation structure of savanna ecosystems. Proper fire management practices can help restore degraded savannas and conserve key species. Community-based fire management can also improve the effectiveness of fire management frameworks in protected areas.
- Senior at What Age: Benefits & Eligibility Guide - March 29, 2025
- Unlocking Senior Benefits: How Old is a Senior? Your Complete Guide - March 29, 2025
- Master Russian Politeness:A Guide to Saying Please - March 29, 2025